前言
● 下面是之前学习ES6 classes的代码
class PersonCl {
constructor(fullName, birthYear) {
this.fullName = fullName;
this.birthYear = birthYear;
}
calcAge() {
console.log(2037 - this.birthYear);
}
greet() {
console.log(`你好${this.fullName}`);
}
get age() {
return 2037 - this.birthYear;
}
set fullName(name) {
if (name.includes(' ')) this._fullName = name;
else alert(`${name} is not a full name!`);
}
get fullName() {
return this._fullName;
}
//静态方法
static hey() {
console.log('哈喽!');
}
}
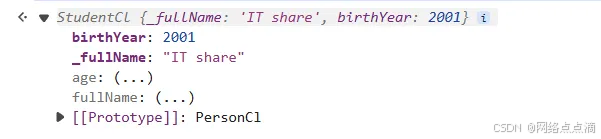
● 和之前一样,我们创建一个学生的类继承Personcl,并且学生也有自己独特的属性
class StudentCl extends PersonCl {}
const ITshare = new StudentCl('IT share', 2001);
我们即使没有写任何的构造函数,也可以直接继承父类
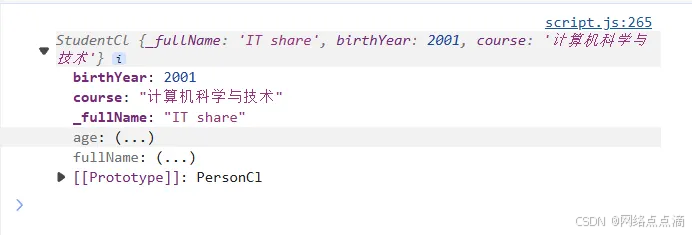
● 现在我们尝试写构造函数来给学生赋予新的属性,并且可以让学生继承父类的方法
class StudentCl extends PersonCl {
constructor(fullName, birthYear, course) {
//总是需要首先书写
super(fullName, birthYear);
this.course = course;
}
}
const ItShare = new StudentCl('IT share', 2001, '计算机科学与技术');
console.log(ItShare);
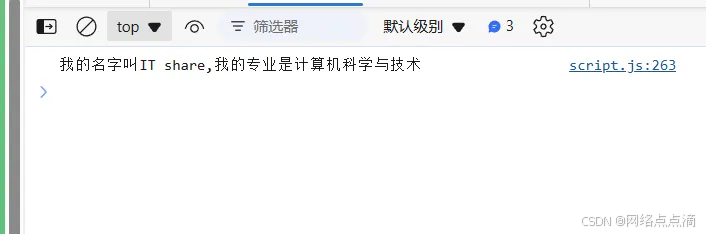
● 可以像上一章一样再学生类中添加新的方法
class StudentCl extends PersonCl {
constructor(fullName, birthYear, course) {
//总是需要首先书写
super(fullName, birthYear);
this.course = course;
}
introduce() {
console.log(`我的名字叫${this.fullName},我的专业是${this.course}`);
}
}
const ItShare = new StudentCl('IT share', 2001, '计算机科学与技术');
ItShare.introduce();
● 当然,父类中的计算年龄的方法也同样适用
class StudentCl extends PersonCl {
constructor(fullName, birthYear, course) {
//总是需要首先书写
super(fullName, birthYear);
this.course = course;
}
introduce() {
console.log(`我的名字叫${this.fullName},我的专业是${this.course}`);
}
}
const ItShare = new StudentCl('IT share', 2001, '计算机科学与技术');
ItShare.introduce();
ItShare.calcAge();

声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。

评论(0)